|
What's ADSL?
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
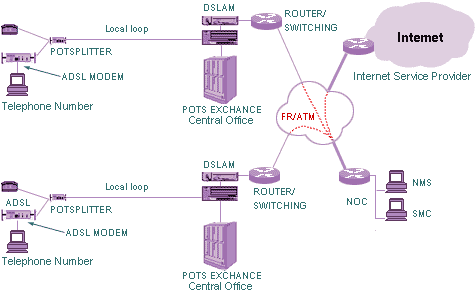
ADSL or Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line Technology is a high speed data transmission along twisted copper pair (telephone lines) through frequency range not used by telephone calls. It means during data transmission through ADSL network calls can be made and received.
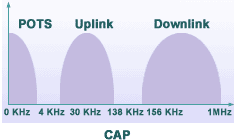
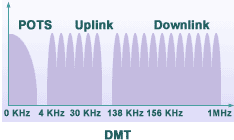
ADSL Technology ADSL belongs to XDSL family. Its unique feature is asymmetric data transmission, with downstream transmission from server to subscriber at the rate of 64 Kbps - 8 Mbps and upstream transmission from subscriber to server at the rate of 64 Kbps - 1.5 Mbps, depending on the type, quality and distance of copper wires. At present, there are two types of modulations: carrier amplitude/phase (CAP) modulation and discrete multi-tone (DMT) modulation. With both types of modulations, frequencies are divided into 3 ranges. POTS, uplink and downlink.
Applications ADSL technology mainly uses TCP/IP protocol on the Internet. It has been developed from ATM technology. Therefore, it has great capability for multimedia applications: Multi-Service, Tele Education, Fast Internet, Distance Learning, Telecommuting, News Clipping, Near VDO on Demand and Entertainment on Demand The Multi-service system enables subscriber to choose the service to suit his requirements, e.g. use of Fast Internet or Education service for searching something.
Benefits: - Multi-service
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Note from: http://www.thenetsec.com | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||