Page 34 - 2025S
P. 34
UEC Int’l Mini-Conference No.54 27
Table 1: Comparison of Dynamic Multi-objective Optimization Techniques
Method HV Performance Change Response Implementation Key Limitations
Standard DNSGA- Medium Slow Simple Fixed parameters
II [3]
Memory-based [6] Medium Medium Moderate Archive manage-
ment
Prediction-based [7] High Fast Complex Training overhead
Random Immi- Low Fast Simple Convergence disrup-
grants [5] tion
Proposed High Fast Moderate Computational
cost
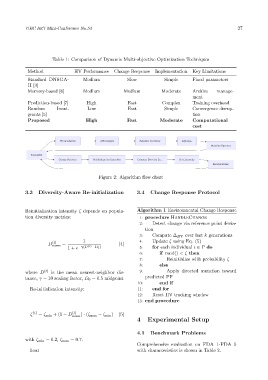
Figure 2: Algorithm flow chart
3.3 Diversity-Aware Re-initialization 3.4 Change Response Protocol
Reinitialization intensity ζ depends on popula- Algorithm 1 Environmental Change Response
tion diversity metrics: 1: procedure HandleChange
2: Detect change via reference point devia-
tion
3: Compute ∆ HV over last k generations
1 4: Update ζ using Eq. (5)
(t)
D norm = (4)
1 + e −γ(D (t) −D 0 ) 5: for each individual i ∈ P do
6: if rand() < ζ then
7: Reinitialize with probability ζ
8: else
where D (t) is the mean nearest-neighbor dis- 9: Apply directed mutation toward
tance, γ = 10 scaling factor, D 0 = 0.5 midpoint. predicted PF
10: end if
Re-initialization intensity: 11: end for
12: Reset HV tracking window
13: end procedure
ζ (t) = ζ min + (1 − D (t) ) · (ζ max − ζ min ) (5)
norm
4 Experimental Setup
4.1 Benchmark Problems
with ζ min = 0.2, ζ max = 0.7.
Comprehensive evaluation on FDA 1-FDA 5
float with characteristics is shown in Table 2.